Approach 1-Integrating Gitlab repository with Cloud Build Triggers via webhook and creating CI/CD…
Approach 1-Integrating Gitlab repository with Cloud Build Triggers via webhook | CI/CD pipelines with GKE
Hello everyone 👋, In this blog we will build the code from Gitlab repository and deploy our code to Google Kubernetes Engine by integrating it with Cloud Build.

As we can see Cloud Build Triggers doesn't give direct option to build our code from Gitlab repository . Only Github, Bitbucket and Google Source Repository are available. So for selecting Gitlab as a source repository , we have 2 approaches.
Approach 1 — In order to build our code with Gitlab, we need to introduce Gitlab webhooks to build our code and to automate our builds in response to webhook events.
Approach 2 — (Best Practise). By creating Mirroring of Repository between Gitlab and Google Cloud Source Repository to use advanced features with our builds that CSR(Cloud Source Repository) provides . In this method we will first mirror the Gitlab repository, then we will select the Cloud Source Repository as a source in our Cloud Build triggers.
In this Blog, we will discuss approach No 1

Overall Flow (Approach 1)
- So whenever we push our code to Gitlab repository, the request will first go to Gitlab webhook.
- Gitlab webhook forwards the request to GCP Secret Manager .
- Cloud Build will fetch the value of secret(Private keys) from GCP Secret Manager.
- Now the steps mentioned in Cloud Build inline yaml will be executed in the container.
— CICD pipeline steps will be look like:
- copy the SSH keys.
- Clone the Gitlab Repository.
- Build the code and Tag the image.
- Push it to Google Container Registry and deploy into GKE Cluster.
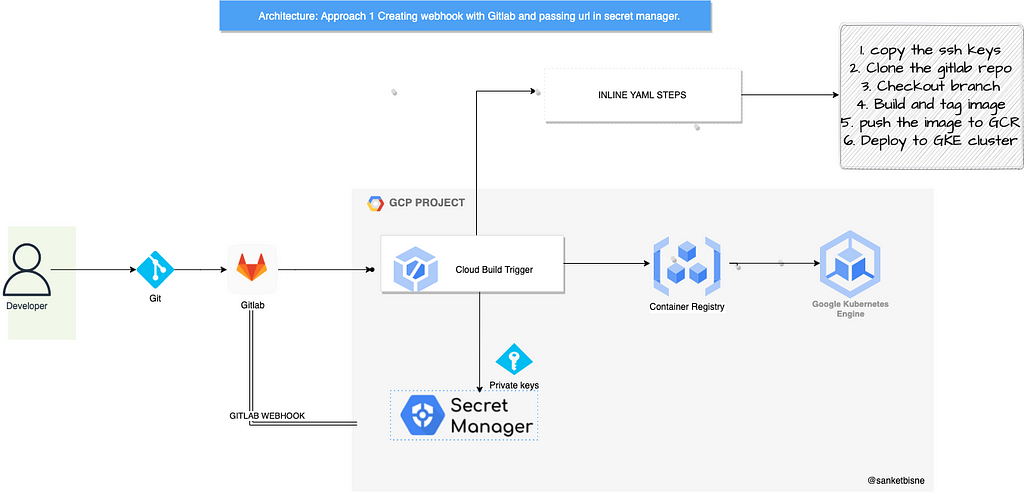
Webhook triggers can authenticate and accept incoming webhook events. These events are sent to a custom URL which a llows us to directly connect to external systems and external source code management systems such as Bitbucket.com, Bitbucket Server or Gitlab to Cloud Build through webhook events.
With webhook triggers, we can define an inline build configuration file rather than specifying a source when creating our trigger. The inline build configuration enables us to have control over git operations and define our rest of the builds.
To start our journey with Gitlab and Cloud Build , below are the steps that we will follow going forward.
Prerequisite: We need to enable API for Cloud Build, Secret Manager, GKE and the services used in this tutorial. and we need a VPC for subnets, service account with least privilege permissions and a GKE Cluster created.
Let's provision our infrastructure through Terraform.
Below repository walks us through shell scripts to enable API's and terraform code to build following resources.

Clone the below repository and checkout to "webhook" branch
git clone https://github.com/sanketbisne/gcp-terraform-resources.git
cd gcp-terraform-resources
git checkout webhook
GitHub - sanketbisne/gcp-terraform-resources
Steps:
1. Preparing our code.
2. Generating our SSH keys for authentication purpose.
3. Storing the generated SSH keys in Secret Manager . We will store our public key in Gitlab and private key in GCP Secret Manager .
4. Creating Inline build configuration file.
5. Pushing our code to Gitlab and triggering Cloud Build to build and deploy our code changes.
1. Preparing our code
Lets's start b y creating a Gitlab repository and push our code inside it.
2. Generating our SSH keys for authentication purpose:
Now let's create our SSH keys in order to authenticate our connection to Gitlab. After creating SSH keys we need to add our private keys inside GCP Secret Manager and our public keys inside Gitlab when creating our webhook.
Then we need to retrieve our SSH keys in your inline build configuration specified in Cloud Build Trigger and specify a version under it.
Creating our SSH keys by the following command.
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -N '' -C gitlab.com -f <our gitlab id>
We can see that 2 keys are been generated . ie public key and private keys

Now we need to add our .pub key inside ssh keys section of Gitlab.
Go to Gitlab >> Profile >> Preferences >> SSH Keys
Click on .pub file and copy the keys and add it to Gitlab section.

3. Storing the generated SSH keys. Public key in Gitlab and private key in secret manager:
Secret: We will need a secret to authenticate our incoming webhook events.
- After storing our public keys in Gitlab , now we need to store our private keys in GCP Secret Manager. This private keys are used to invoke our build and it validates and authorise our incoming webhook events to Cloud Build.
- Click on upload file(our private key)which we have generated earlier , it will automatically populat e the secret values.

Click on create secret , after secret is created it will have a default version v1, which we have to select when we will create our Cloud Build triggers.

As soon as selected our existing secret, we can see a webhook URL preview. Our URL will contain an API key generated by Cloud Build and our secret. Our webhook URL will look like below:
https://cloudbuild.googleapis.com/v1/projects/<$PROJECT_ID>/triggers/s8-gitlab-cloudbuild-trigger:webhook?key=<SECRET VALUE>secret=-----BEGIN%20OPENSSH%20PRIVATE%20KEY-----<SECRET_VALUE>0A-----END%20OPENSSH%20PRIVATE%20KEY
This completed url needs to be added into the Gitlab webhook , we will see in the upcoming steps.
Click on inline yaml and add the following details under the substitution as _TO_SHA$ = (body.after) and _BRANCH$ =(body.ref)variables and
filters like master / dev branch.
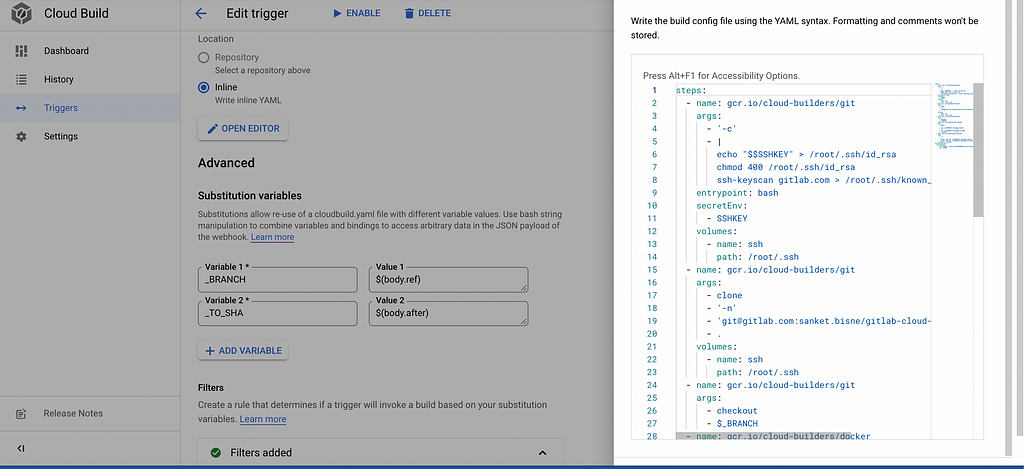
Click on Filters, add the branch you need to trigger whenever there is push in branch. Because by default if we doesn't specify any branch in filter, it will build the code from any branch.
Go to filters and add the following values

Variable=_BRANCH
Operator=matches
Regex Value=refs/heads/main
4. Creating our Inline Build inline configuration file.
These steps add the ssh keys , clone the repository , checkout into main branch, build the docker image , tag the image and push the image into Google Container Registry and finally deploys image to GKE cluster.
Copy the webhook URL Preview that we have generated in the earlier step and add into the Gitlab webhook , so whenever there is event changed , Cloud Build will trigger and execute the above steps.
- Go the repository
- On left side there will be Setting >> webhook
- Copy the webhook url and paste in URL Section. click on checkbox according to your requirements.
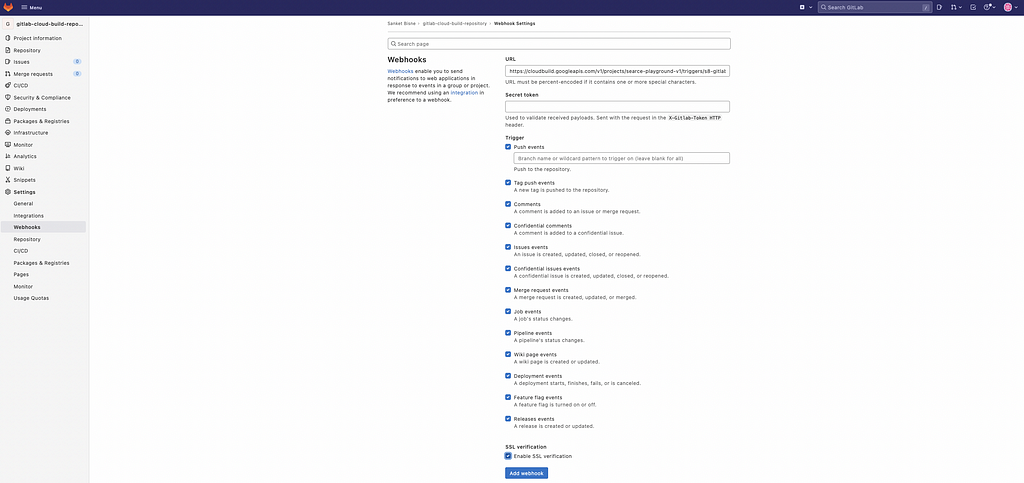
Click on test connection we will receive the following HTTP 200 OK Code.

Now we are ready to push our code into Gitlab. As soon as we push our code into Gitlab, Gitlab webhook will call Cloud Build trigger which has ssh keys stored in GCP Secret Manager, the secrets will be fetched and our Cloud Build trigger will execute the steps specified in inline editor config.

Limitations:
The features that are not available if we select the webhook approach
- we don't have the control over $SHORT_SHA, and other features that we get when we select source as Github, Bitbucket and Google Source Repository.
- We dont have option to run triggers manually in GCP based on webhook event, this can be only done from Gitlab .
- For ea ch application we need to maintain secrets which is not feasible and scalable solution.
- This Approach uses inline yaml file in which all the steps are written.This is not recommended because we don't have control to build the image from any central repository.
- There are only few features available if we want to use substitution variables . we need to enter the values like _TO_SHA$ = (body.after) and _BRANCH$ =(body.ref)also if we want to modify anything then we need to add git commands in entry point to Cloud Build while executing steps, which is another complex workaround.

- Tag based and Branch based Triggers. If we want to trigger our pipeline based on the git tags like PATCH_1 or want to use asterisk like PRODUCTION_RELEASE* . This is not supported here beca use we are using inline build yaml .
This Tutorial was all about building the Gitlab repo code via webhook approach.
In Part 2, we will be discussing our 2nd approach on how we can mirror the Gitlab and google cloud repository to use advance feature that webhook lacks and how to automatic trigger our pipelines to deploy our workloads to kubernetes cluster for development and production environments.
Summary
In this blog, we learnt how to Create Cloud Build triggers with Gitlab as a source repository using webhook approach. Now in next blog we will see how to mirror Gitlab and CS R and use CSR as a Source Repository.
References:
1. https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/integrations/webhook_events.html
2. https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/integrations/webhooks.html
3. https://cloud.google.com/build/docs/automating-builds/build-repos-from-gitlab
Have Any Questions? : If you have any questions, I'll be happy to read them in the comments. Follow me on medium or LinkedIn.
Thank you , have a great day ahe ad 😊
Approach 1-Integrating Gitlab repository with Cloud Build Triggers via webhook and creating CI/CD… was originally published in Google Cloud - Community on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Comments
Post a Comment